There is a difference between outstanding and issued shares, but some companies might refer to outstanding common shares as issued shares in their reports. When a company’s entire liabilities exceed its total assets, its book value is negative. When looking at the financial statements of a business, look for information about stockholders’ equity, also known as owner’s equity.

The Difference Between Market Value per Share and Book Value per Share
Book value per share (BVPS) measures the book value of a firm on a per-share basis. BVPS is found by dividing equity available to common shareholders by the number of outstanding shares. It may not include intangible assets such as patents, intellectual property, brand value, and goodwill. It also may not fully account for workers’ skills, human capital, and future profits and growth.
- Even though book value per share isn’t perfect, it’s still a useful metric to keep in mind when you’re analyzing potential investments.
- A company can use a portion of its earnings to buy assets that would increase common equity along with BVPS.
- It excludes value of intangible assets from book value of shareholders’ equity used in the normal book value per share calculation.
- The ratio may not serve as a valid valuation basis when comparing companies from different sectors and industries because companies in other industries may record their assets differently.
- Investors should do extensive study and consider a variety of aspects before making a selection, just like they should with any other investment.
Why Is the Price-to-Book (P/B) Ratio Important?
Value investors look for relatively low book values (using metrics like P/B ratio or BVPS) but otherwise strong fundamentals in their quest to find undervalued companies. A P/B ratio of 1.0 indicates that the market price of a share of stock is exactly equal to its book value. For value investors, this may signal a good buy since the market price generally carries some premium over book value.
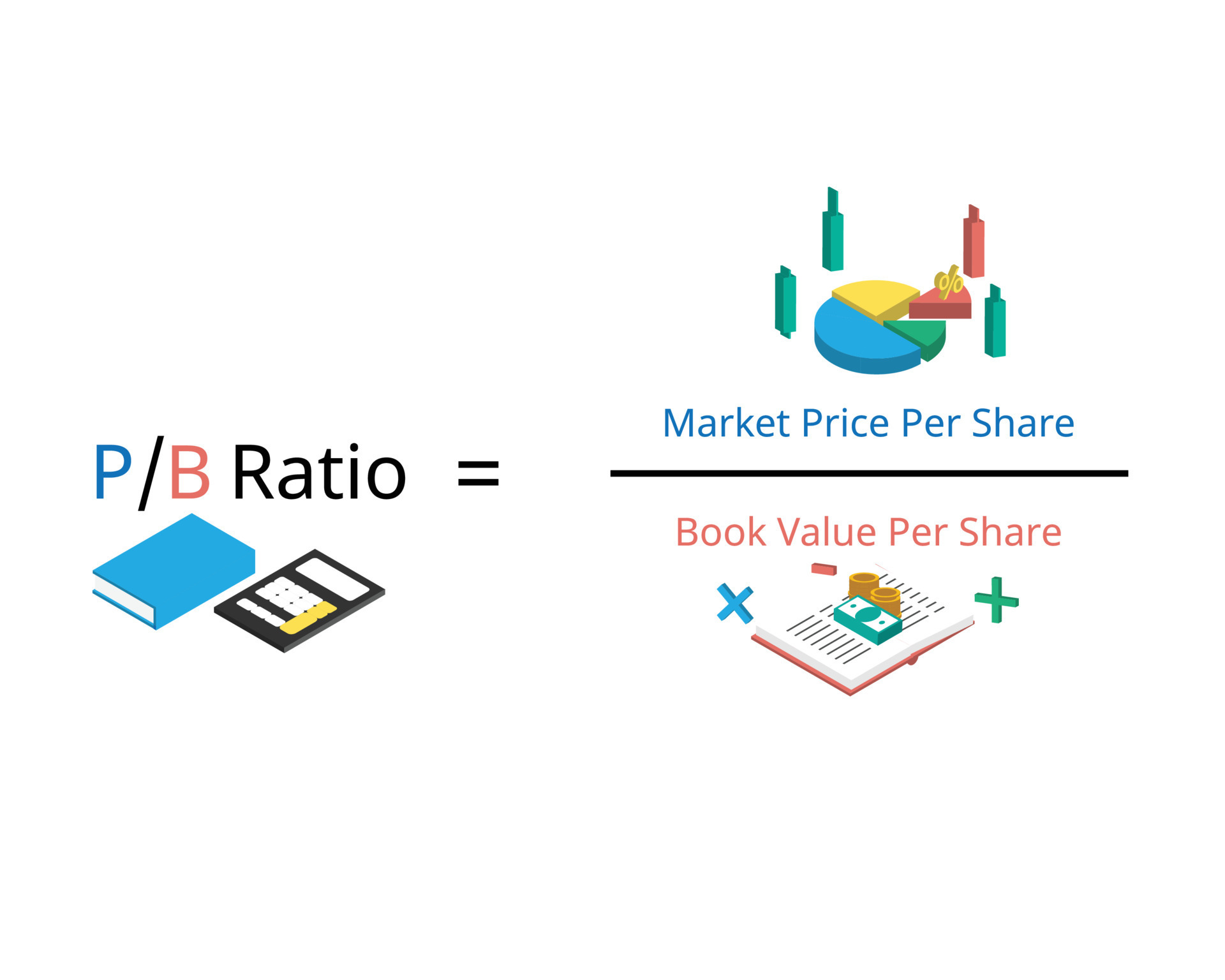
Formula and Calculation of the Price-to-Book (P/B) Ratio
There is also a book value used by accountants to value the assets owned by a company. This differs from the book value for investors because it is only used internally for managerial accounting purposes. BVPS is more relevant for asset-heavy companies, such as manufacturing firms, where physical assets constitute a significant portion of the balance sheet.
A company’s stock buybacks decrease the book value and total common share count. Stock repurchases occur at current stock prices, which can result in a significant reduction in a company’s book value per common share. If XYZ can generate higher profits and use those profits to buy more assets or reduce liabilities, the firm’s common equity increases. If, for example, the company generates $500,000 in earnings and uses $200,000 of the profits to buy assets, common equity increases along with BVPS. On the other hand, if XYZ uses $300,000 of the earnings to reduce liabilities, common equity also increases.
Companies Suited to Book Value Plays
You won’t get this information from the P/B ratio, but it is one of the main benefits of digging into the book value numbers and is well worth the time. That said, looking deeper into book value will give you a better understanding of the company. In some cases, a company will use excess earnings to update equipment rather than pay out dividends or expand operations. This means that each share of the company would be worth $8 if the company got liquidated.
One must consider that the balance sheet may not reflect with certain accuracy, what would actually occur if a company did sell all of their assets. Investors can calculate it easily if they have the balance sheet of a company of interest. Investors can compare BVPS to a stock’s market price to get an idea of whether that stock is overvalued or undervalued. This formula shows the net asset value available to common shareholders, excluding any preferred equity.
Besides his extensive derivative trading expertise, Adam is an expert in economics and behavioral finance. Adam received his master’s in economics from The New School for Social Research and his Ph.D. from the University of Wisconsin-Madison in sociology. He currently researches and teaches economic sociology and what are sundry expenses definition meaning example the social studies of finance at the Hebrew University in Jerusalem. The company’s current stock price per share is divided by its book value per share (BVPS) to come up at this ratio. ConclusionWhen investors need to assess a company’s valuation, the price-to-book, or P/B, ratio is a helpful financial tool.
Now, let’s say that Company B has $8 million in stockholders’ equity and 1,000,000 outstanding shares. Using the same share basis formula, we can calculate the book value per share of Company B. Nevertheless, most companies with expectations to grow and produce profits in the future will have a book value of equity per share lower than their current publicly traded market share price. Often called shareholders equity, the “book value of equity” is an accrual accounting-based metric prepared for bookkeeping purposes and recorded on the balance sheet. If a company’s share price falls below its BVPS, a corporate raider could make a risk-free profit by buying the company and liquidating it. If book value is negative, where a company’s liabilities exceed its assets, this is known as a balance sheet insolvency.
Alongside her accounting practice, Sandra is a Money and Life Coach for women in business. By multiplying the diluted share count of 1.4bn by the corresponding share price for the year, we can calculate the market capitalization for each year. The formula for BVPS involves taking the book value of equity and dividing that figure by the weighted average of shares outstanding.


